Health Technology Assessment in India- Attached Office Under Department of Health Research
1. Background
Importance of Health Technology Assessment
The Government of India is committed to extend healthcare services to its 1.44 billion population and is constantly making endeavours to provide affordable and quality healthcare. The government strives to provide affordable healthcare to its citizens within the available resources with optimal resource allocation.
Health Technology Assessment (HTA), is a widely used methodology globally, for evidence generation for decision making in healthcare sector and for optimization of resource utilization in health. HTA provides systematic evaluation of properties, effects and/or impacts of health technologies or interventions. The assessment is conducted by interdisciplinary groups using explicit analytical frameworks, drawing on clinical, epidemiological, health economic and other information and methodologies. It may be applied to evaluate health interventions andpublic health programmes, priority setting in health care, identifying cost effectiveness thresholds for medicines and other technologies based on their cost–effectiveness, and for guiding the development of clinical guidelines. “Health technology or Health intervention” refers to an application of organized knowledge and skills in the form of diagnostics, devices, drugs including their formulations and delivery systems, vaccines, procedures, novel therapeutics, health programmes and systems developed to address a health problem and improve quality of lives including digital technologies”.
Department of Health Research, MoHFW initiated a pilot programme on Health technology Assessment (HTA) in April 2017 for evaluation of appropriateness and cost effectiveness of both existing and new health technologies in the country as part of “Research Governance” mandate of the Department. In June 2021, the HTA was approved as a sub scheme under the umbrella Scheme of Human Resource and Capacity Development.
Office of the Health Technology Assessment in India (HTAIn) has been approved for establishment as an attached office with 4 divisions on 9th May 2023. The Department of Expenditure has also approved the constitution of the attached office in Department of Health Research with creation of 15 scientific and administrative posts.
2. Aim and Objectives of Attached Office
HTAIn is entrusted with the responsibility to analyses health technologies viz. medicines, devices and health programmes for its cost-effectiveness, clinical-effectiveness and equity issues by means of Health Technology Assessment (HTA), and in turn help in decision making for an efficient use of the limited health budget and provide people access to the quality health care reducing their out-of-pocket expenditures (OOPs) on health.
Objectives
•To undertake HTA studies aiming at maximizing health in the population, reducing out of pocket expenditure (OOP) and reducing inequity. • To support the process of decision-making in health care at the Central and State policy level by providing reliable information based on scientific evidence. • Develop systems and mechanisms to assess new and existing health technologies by a Transparent and inclusive processes • To appraise health interventions and technologies based on available data on resource use, cost, clinical effectiveness, and safety. • To collect and analyse evidence in a systematic and reproducible way and ensure its accessibility and usefulness to inform health policy. • Disseminate research findings and resulting policy decisions to educate and empower the public to make better informed decisions for health.
3. Structure of the Health Technology Assessment in India Attached Office of DHR
The Health Technology assessment has a Board chaired by the Member NITI Aayog and consisting of ex-officio members and domain experts. It is being assisted by Technical Appraisal Committees and a Secretariat, an attached office of Department of Health Research, to undertake its functions. Resource centres have been established across the Country to Undertake HTA studies and help in Implementation by the States.
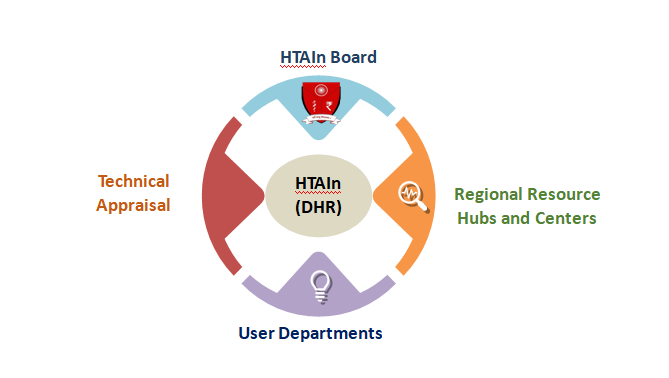
The Four Divisions are:
i. Clinical-effectiveness Assessment Division- assessesclinical effectiveness of medical devices, vaccines & drugs, diagnostics, intervention procedures and digital health technologies. ii. Economic Assessment Division - assesses cost effectiveness of medical devices, vaccines & drugs, diagnostics, intervention procedures and digital health technologies. iii. Technology Integration in Public Health programs Division - facilitates integration of the health technologies recommended by the HTA Board into the public health programmes to ensure accessibility, affordability and equity, for example level of health system for which technology is appropriate. iv. Coordination, Communication and Administration Division- coordinates and communicates with broader stakeholder groups including Ministries/Departments other than health and with academia and private sector. The divisions will comprise of Scientists, Administrators and consultants at various levels. For more details, visit us at https://htain.dhr.gov.in
HTA Resource Hubs
1. Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh. 2. Indian Institute of Public Health (IIPH), Gandhinagar 3. National Institute for Research in Reproductive Health (NIRRH), Mumbai 4. Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry. 5. National Institute of Epidemiology, Chennai 6. Indian Institute of Public Health (IIPH), Shillong 7. National Institute for Research in Tuberculosis (NIRT), Chennai 8. Regional Medical Research Center (RMRC), Bhubaneswar
HTA Resource Centres (RRCs)
Resource Centres have been established in Government research institutes to conduct HTA and other multi-centric studies allocated by HTAIn Secretariat. 1. Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST), Trivandrum 2. National Centre for Disease Informatics and Research, Karnataka 3. National Institute of Virology, Pune 4. State Cancer Institute and King George Medical University, Lucknow 5. Indian Institute of Public Health, Hyderabad 6. Kalam Institute of Health Technology, Visakhapatnam 7. All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Rishikesh 8. Indian Institute of Technology-Delhi 9. All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Jodhpur 10. Indian Institute of Science (IISc.) Bengaluru 11. Institute of Medical Sciences, Banaras Hindu University (BHU), Varanasi 12. Dr Rajendra Prasad Government Medical College, Kangra 13. Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur 14. Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai 15. Armed Forces Medical College, Pune 16. All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Bhopal 17. Indian Institute of Public Health-Delhi 18. All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) Guwahati 19. Prasanna School of Public Health (PSPH) Manipal 20. All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) New Delhi
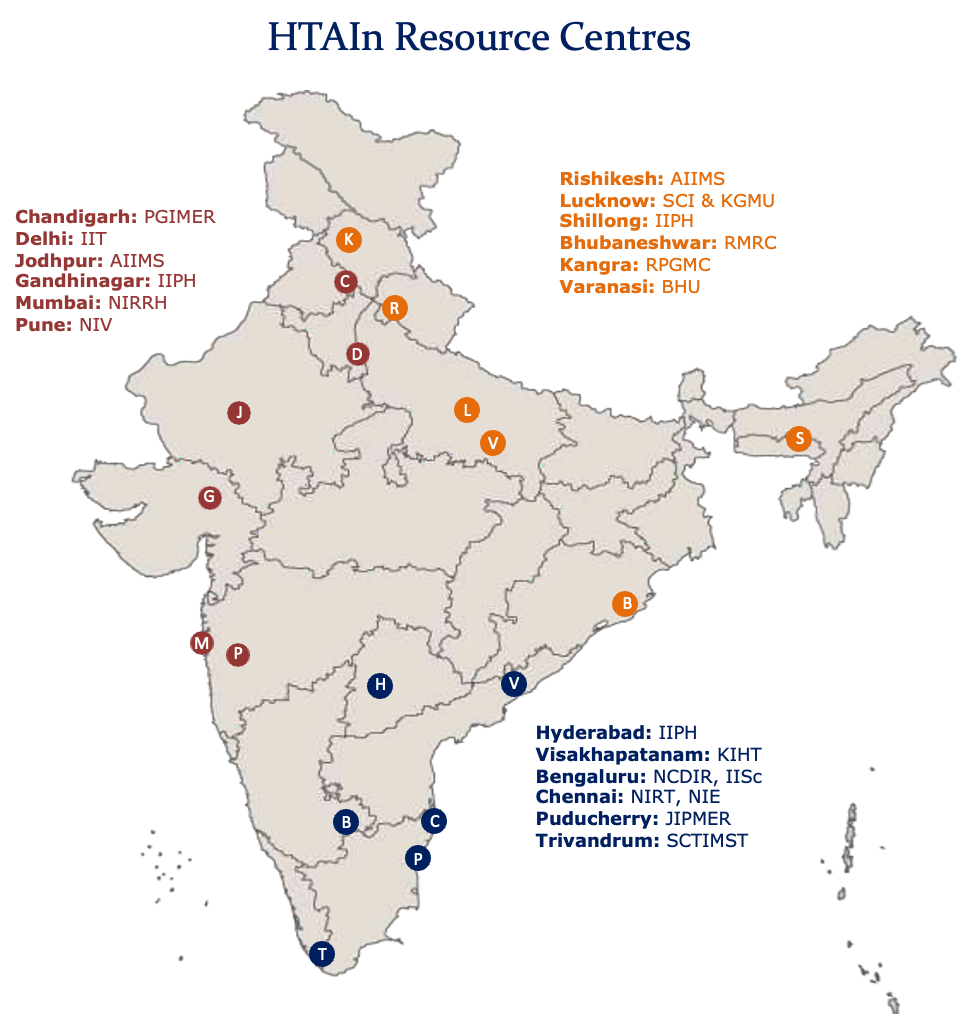
Figure 1: HTAIn Resource Centres
8 HTAIn Resource Hubs in Green and 20 Resource centres in Orange
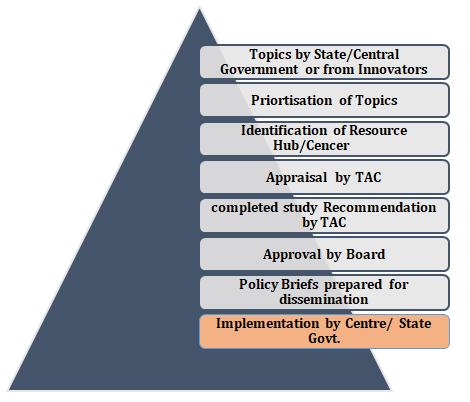
5.Process of HTAIn
1.The User Department send their topic(s) to the Secretariat according to their priority area to conduct an assessment. 2.The topic is prioritized by the HTAIn Secretariat. After prioritization, Secretariat present the topic(s) to theTAC and a suitable Resource Hub/Centres is identified to allocate those topic(s) to conduct the HTA study. 3.The respective Resource Hub/Centres then submit a study proposal that contains the policy question(s), research question(s), objective(s), PICO, methodology, timeline, and the proposed Model/decision tree. 4.The proposal is submitted to the TAC for approval. 5.After the appraisal and approval of the proposal by the TAC, Resource Hubs/Centres conduct the HTA study and after completion of the study submit the Outcome Report to TAC forapproval. 6.Once the outcome report is approved by the TAC, it is submitted to the Board for final approval. 7. Then a policy brief is prepared for dissemination and sent to the Central/State Government for implementation.
HTAIn Logo
The logo of Health Technology Assessment in India (HTAIn) is in the form of a shield which represents the protecting role of HTAIn towards its citizens from the financial hardships arising out of health care seeking. The top of the shield is marked with Ashok Chakra, depicting the allegiance of HTAIn towards the constitutional values and the nation. The Rod of Asclepius and the symbol of the Indian Rupee are placed side by side below the National Emblem; as while making a decision about the cost-effectiveness of an intervention, HTAIn gives due consideration to both public health potential and the costs associated with the intervention. “ सर्वेःसन्तुनिरामयाेः” is scripted in Devnagri script on a ribbon, which means “Let all be healthy”, and expresses the devotion of HTAIn towards the values of Universal Health Coverage (UHC).

Policy Briefs
Policy Brief vol 1 (Link to pdf)
Policy Brief vol 2 (Link to pdf)
Guidelines HTAIn
Guidelines (Link to pdf (712.94KB))
HTAIn Videos
1. Introduction to HTAIn
2. Journey of HTAIn
Concerned Officers dealing with HTAIn Scheme
- List of HTAIn Board Members (Link to pdf (65.33KB))
- List of HTAIn TAC Members (Link to pdf(410.04KB))
- Director in charge: Shri Murari lal Sharma (ml[dot]sharma66[at]nic[dot]in, +91 11 23736218)
- Scientist in charge: Dr. Kavitha Rajsekar (kavitha[dot]rajsekar[at]nic[dot]in, +91 11 23736906)